A Guide to Zoning Laws and Their Impact on Commercial Properties


Understanding commercial zoning laws is essential for anyone involved in real estate, whether you’re an investor, developer, or business owner. These laws dictate how land can be used, influencing everything from property values to development opportunities.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through what commercial zoning laws are, why they matter, and how they impact your real estate investments, providing a deep dive into everything you need to know about how zoning laws for commercial buildings are created and used. By the end, you’ll have a strong grasp on how these regulations shape the marketing - and how to use this knowledge to your advantage.
What are Commercial Zoning Laws and Why Do They Matter?
Commercial zoning laws are local government regulations that divide a community into zones or districts, each with its own set of rules about how the land can be used. These laws ensure that new developments fit in with their surroundings and contribute positively to the community’s overall plan. They help control building density, preserve neighborhoods, and guide urban growth, all while protecting property values and public safety.
Understanding the zoning laws commercial buildings must adhere to is essential for investors and developers to navigate local regulations and unlock a property's full potential, making the difference between a profitable venture and a regulatory headache.
Ultimately, being well-versed in zoning regulations gives you the insight needed to assess a property's potential, align your project with local plans, and avoid costly surprises down the road.
Commercial Zoning Reports
A commercial zoning report provides a snapshot of the zoning conditions of a property and is an integral part of the due diligence process when buying commercial real estate:
- Current zoning classification
- Basic property information such as parcel number and current and prior uses
- Setback and parking requirements
- Height and floor measurements
- Notice of variances related to special permits and conditions
- Notice of outstanding code violations such as zoning, fire, and building

How Zoning Laws for Commercial Buildings are Created
Zoning laws for commercial buildings aren’t arbitrary - they’re the result of careful planning and community input. Local governments start with a comprehensive master plan that outlines the area's vision for growth and development. Planners take into account current land use, infrastructure needs, environmental factors, and community goals to establish zoning ordinances that reflect both present and future needs.
These ordinances lay out guidelines on building height, density, setbacks, parking requirements, and permissible land uses. For instance, a downtown district might be designated for mixed-use development to encourage both residential and commercial activity, while industrial areas might have stricter guidelines to limit environmental impact. Public input also plays a critical role; through community meetings and public hearings, residents and business owners can share their views on proposed zoning changes, ensuring that the final regulations serve the broader community interest.
Types of Commercial Zoning and Their Uses
Commercial zoning is far from one-size-fits-all. Different types of commercial zoning are tailored to accommodate various business activities and community needs.
Here are some of the most common commercial zoning types:
- Retail Zoning: This zoning is designed for shopping centers, restaurants, and storefronts. For example, a strip mall in a C-1 zone might allow for small retail stores, but it typically restricts heavy industrial use. Retail zoning is intended to support consumer-facing businesses that drive foot traffic and contribute to the local economy.
- Office Zoning: Office zoning is meant for professional services and corporate headquarters. Areas designated for office use, such as a C-2 or B zone, typically allow for coworking spaces, business parks, and other office-related uses. These zones are usually found in central business districts or suburban office parks, where infrastructure and accessibility are key.
- Industrial Zoning: Industrial zones cater to manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution centers. Zoning in these areas, often marked as I-1 or I-2, sets guidelines for production activities, storage facilities, and logistics hubs. These zones are critical for maintaining an efficient supply chain and supporting local employment in manufacturing.
- Mixed-Use Zoning: Mixed-use zoning permits a combination of residential, commercial, and sometimes even industrial uses within a single area. This flexible zoning is popular in urban centers, where integrating different functions can enhance community vibrancy and reduce commuting times.
Each type of commercial zoning comes with its own set of permitted uses and restrictions, so it’s essential to verify local zoning ordinances before investing or developing. This not only helps ensure compliance but also maximizes the potential of your property by aligning it with the most suitable use.

Key Zoning Restrictions for Commercial Properties
Even within a specific zoning classification, there are often additional restrictions that can impact a property’s development potential. These restrictions are designed to balance the needs of property owners with those of the community. Before moving forward with a project, it’s important to review the specific zoning restrictions that apply to your property to avoid surprises and ensure your plans align with local regulations.
Some key zoning restrictions to keep in mind include:
- Building Height and Density: Many municipalities set limits on how tall a building can be or how many units can be built on a given parcel. These restrictions are designed to maintain the character of a neighborhood and prevent overdevelopment.
- Setback Requirements: Setbacks determine the minimum distance a building must be from property lines or streets. These requirements help ensure adequate light, air, and privacy for surrounding properties.
- Parking and Access: Zoning laws often mandate a minimum number of parking spaces for commercial properties. This is especially important for retail and office spaces, where customer and employee access is critical.
- Signage Regulations: Local ordinances may limit the size, placement, or lighting of signs to maintain aesthetic standards and minimize distractions or safety hazards.
- Environmental and Noise Restrictions: Some zoning codes include measures to protect the local environment or manage noise levels, particularly in areas close to residential neighborhoods

Understanding Zoning Variances & Rezoning Commercial Properties
Sometimes, the strict requirements of commercial zoning laws can limit the potential uses of a property. In these cases, zoning variances and rezoning come into play.
Zoning Variances
A variance is a legal exception to the zoning rules granted by a local government. It allows a property owner to deviate from certain requirements when strict adherence would cause undue hardship. For instance, a property owner might seek a variance for a building that slightly exceeds the height limit due to unique architectural features or existing conditions that make compliance impractical.
Rezoning
Rezoning is the process of changing a property’s zoning classification altogether. This can open up new opportunities by permitting uses that were previously not allowed. For example, a parcel initially zoned for industrial use might be rezoned to allow mixed-use development, significantly boosting its value. However, rezoning is often a lengthy process that requires public hearings and approval from local planning authorities, and there’s no guarantee of success.
Both variances and rezoning can be powerful tools for unlocking hidden potential, but they require careful planning, a clear demonstration of need, and, often, community support. Working closely with local zoning professionals and understanding the process can improve your chances of success when pursuing these options.
Creative Usage of Land Zoning
The strategic and creative use of land zoning offers owners a pathway to increase the property's usage potential and, and in turn, improve its value. Beyond traditional approaches, innovative zoning strategies can unlock hidden potential and create new revenue streams.
Consider these creative options:
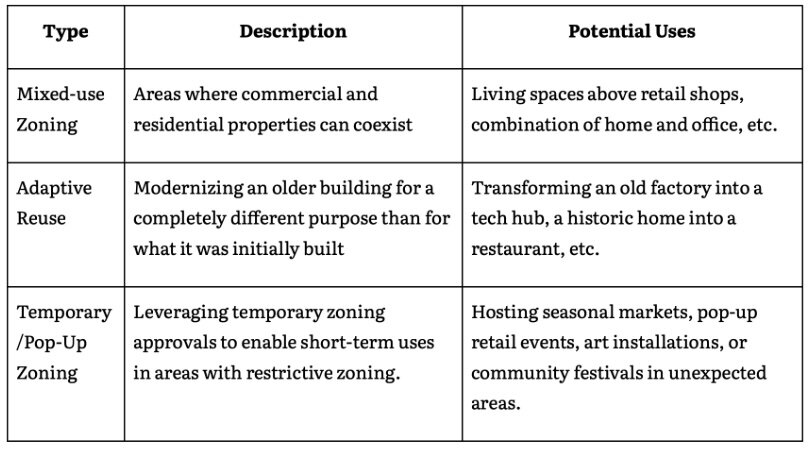

How Commercial Zoning Impacts Real Estate Investments
As a CRE investor, underestimating the impact of commercial zoning would be a mistake. Zoning laws influence the type of development allowed on a property, the potential for future growth, and ultimately, its market value.
Here’s how:









